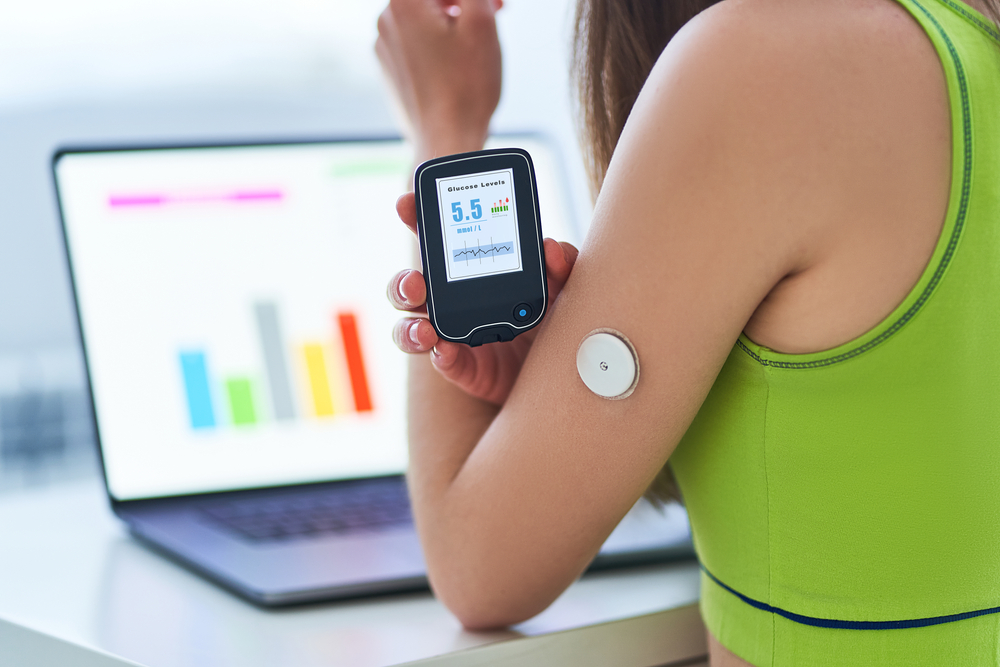
Over the past few years, wearable technology has seen tremendous growth with devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers becoming mainstream. However, a new form of wearable – the wearable patch – is emerging that promises discreet monitoring and could revolutionize healthcare. These small, thin, flexible patches can be attached directly to the skin to continuously track vital signs and other health metrics.
Introduction to Wearable Patches
Wearable patches are essentially thin, flexible sticker-like devices that are applied directly to the skin, often on the chest, arm or back. They are comfortable to wear for long periods of time as they don’t require bulky accessories like watches or wristbands. Some key characteristics of wearable patches include:
– Very thin and flexible designs that conform to body movements. Early patches were usually under 5mm thin.
– Capable of continuously monitoring multiple health signals like ECG, heart rate, respiratory rate, body temperature etc.
– Integrated sensors, processors and wireless radios allow real-time data transmission to smartphones or cloud.
– Battery life of several days to weeks depending on data collection frequency.
– Water resistant designs enable activities like showering with the patch still on.
– Discreet and subtle to wear under clothes without attracting attention.
Potential Applications and Use Cases
With their 24/7 monitoring abilities and discreet form factor, wearable patches open up several promising healthcare applications:
Remote Patient Monitoring – These Wearable Patches can monitor cardiac, respiratory or other vital signs of patients with chronic conditions from home. This allows for early detection of deterioration and reduces hospital visits.
Pre-Hospital Care – Paramedics can attach monitoring patches to assess patients en route to the emergency room, aiding triage and treatment.
Surgery Recovery – Surgical patients can wear patches at homepost-surgery to track recovery trends like wound healing remotely.
Clinical Trials – Researchers can gain deeper insights for drug trials by continuously collecting physiological data from participants with patches.
Athlete Performance – Coaches monitor athlete recovery, workload and fitness levels unobtrusively with skin patches during training.
Military/First Responders – Patches monitor personnel operating in hazardous environments or undertaking strenuous activities to ensure safety.
Continuous Biometric Authentication – Patches could authenticate individuals securely based on their unique biometric signals like ECG for access to high security areas or devices.
Early Stage Companies Exploring Patch Potential
Seeing the vast market potential, startups focused exclusively on wearable patch development have emerged in increasing numbers over the past few years:
– VitalConnect – One of the earliest players with FDA cleared patches monitoring cardiac activity, respiration and more remotely for patient care and clinical research.
– BiOnic – Developing multilayer circuit patch technology to conveniently monitor ECG, temperature and more for fitness, healthcare and industrial applications.
– Quantum Operations – Created Vqpod, a patch for athletes to monitor heart rate variability, breathing patterns and other metrics for optimizing performance and recovery.
– MC10 – Known for low-profile, high-performance stretchable sensor arrays and processors integrated into BodyGuardian patches monitoring fall detection, cardio and more.
– SmartPatch – Focuses on discreet form factors like Band-Aid style patches for continuous patient monitoring in clinical settings and at home with robust data connectivity.
– Profusa – Implantable biosensor technology integrated into patches for non-invasive glucose monitoring, infection detection through tissue color changes and more.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While patch technology holds tremendous promise, there are still some technical challenges to address around long term skin contact, complex data processing capabilities and maintaining high quality wireless connectivity covertly under varied conditions. Data security, privacy and regulatory requirements are also significant aspects to consider.
With advancements in miniaturized electronics, flexible displays, energy harvesting and biomedical sensors though, patches will continue getting smaller, smarter and more capable. Multiday battery life is already feasible. Within a few years, we may see patches perform full lab-grade analysis like blood tests using microfluidics, acquire ultrasound or optical images directly from skin. Genetic based disease risk profiling could also be possible with epigenetic analyses. Ultimately, patches may well transform to sophisticated miniature personal physicians continuously collecting, processing and transmitting health data while keeping users connected to virtual care teams discreetly. The wearable patch is just getting started and will likely play a profound role in shaping healthcare delivery models worldwide in the decades to come.
*Note:
1. Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research
2. We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it