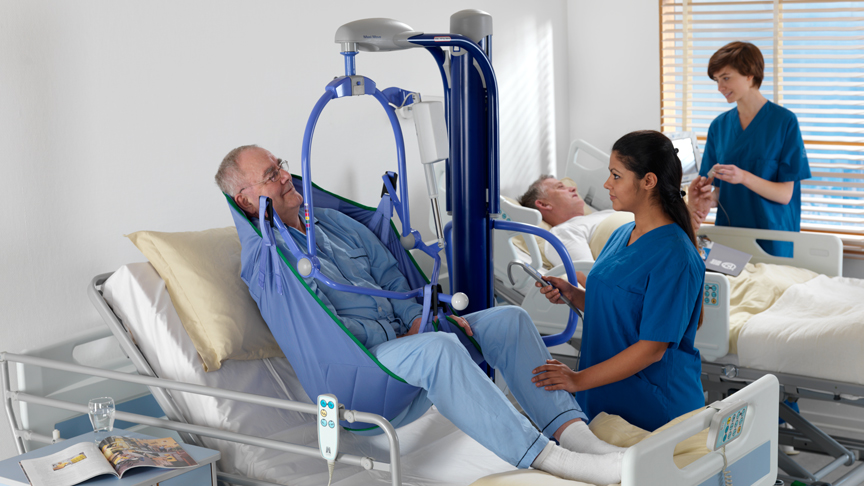
Using the proper patient handling equipment is extremely important for ensuring safety of both patients and caregivers during lifting and mobility tasks. As patients are often unable to move independently due to medical conditions or injuries, they rely on assistance from caregivers for even basic tasks like getting out of bed or being transferred to a wheelchair. However, manually lifting and mobilizing patients poses immense risk of injury to caregivers due to the physical strain involved. Mechanical patient lift handling equipment provides an efficient and risk-free solution.
Importance of Safe Patient Handling
Patient handling has frequently been cited as one of the most physically demanding jobs in the healthcare industry. Studies show that healthcare workers face disproportionately higher rates of musculoskeletal disorders compared to other occupations due to repetitive lifting, transferring and repositioning of patients without using mechanical assistance. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, healthcare support occupations have three times the risk of suffering back injuries compared to other jobs. These injuries can range from minor muscle strains to severe conditions like herniated discs that may require long hospitalization periods and even surgery. Recurrence of such injuries is also common which results in long term disabilities.
Aside from caregiver injuries, manual handling also poses risks for patients. Elderly patients or those with mobility issues are vulnerable to falls, fractures or soft tissue injuries if not lifted or transferred properly using appropriate techniques and equipment. Studies have shown that more than 30% of falls that occur in healthcare facilities are associated with mobility assistance tasks like transfers. Falls, in turn, increase complications, hospitalization costs and extend recovery times for patients.
Safe Patient Mechanical Lift Handling Equipment laws passed in various states in the US recognize these risks and mandate the use of mechanical lifts and lifts in healthcare facilities over dangerous manual handling practices. These laws aim to facilitate a cultural change where patients’ safety and caregivers’ well-being take priority over ease and speed of handling tasks.
Mechanical Lift Equipment for Safe Patient Handling
A variety of mechanical lift equipment has been designed to meet various patient mobility needs in a safe manner:
Ceiling Lifts: Installed on fixed tracks or points on the ceiling, these large overhead lifts have slings or sheets attached to its lifting arm to safely transfer patients between bed and wheelchair. They eliminate the need for caregivers to manually lift and are appropriate for immobile or bariatric patients.
Floor/Standing Lifts: Portable lifts that are mounted on a wheeled base for use throughout the facility. Caregivers attach lift slings or sheets to the lift arms and operate hydraulic mechanisms to raise, lower or transfer patients. Floor lifts provide ease and versatility compared to ceiling lifts.
Power Stand-Assist Lifts: These compact lifts assist in raising patients from sitting to standing position and provide support once standing. They encourage independent mobility and are useful for rehabilitation purposes.
Bathing Systems: Specialized lifts designed specifically for bathing areas with attachments like slings, reusable shower chairs and waterproof stretchers to maintain dignity and comfort during bathing routines.
Lifting Accessories: A range of slings, sheets, straps and harnesses made of breathable, hygienic fabrics to ensure full body support during lifts. Sizes vary to accommodate pediatric to bariatric patients. Slings are color-coded for patients’ specific needs.
Advantages of Using Patient Lifts
– Reduce injuries: Caregivers no longer perform manual lifting, transferring and repositioning tasks. This significantly lowers their risk of developing muscle strains and other musculoskeletal disorders.
– Patient safety: Mechanical lifts provide controlled, gentle mobility of patients with minimal risk of falls, fractures etc. Post-surgery recovery times are reduced with safe mobility practices.
– Staff retention: Safe handling practices help retain qualified caregivers through lower injury rates and job satisfaction of no longer performing high-risk duties manually. This ensures continuity of care.
– Compliance: Use of mechanical lifts complies with patient safety regulations and safe patient handling legislation. Facilities avoid litigation issues related to manual handling injuries.
– Efficiency: Well-trained staff can safety lift and transfer multiple patients quickly with mechanical equipment compared to manual techniques. Saves time spent on handling tasks.
– Adaptability: Lifts are designed for patients across the spectrum – from newborns to bariatric adults. Specific accessories can meet complex clinical needs.
– Cost-effectiveness: Avoidance of injuries, associated lost work, medical bills and lawsuits through safe practices outweighs high upfront costs of equipment over years.
Challenges in Transitioning to Safe Practices
While compelling evidence proves the benefits of using patient lifts, transitioning healthcare facilities fully requires addressing some key challenges:
– High initial equipment costs: Cost of ceiling lifts, multiple floor lifts, slings etc. for an entire facility is substantial. Funding availability is a hurdle.
– Space constraints: Ensuring adequate space clearances for ceiling tracks or maneuverability of floor lifts requires facility modifications in older buildings.
– Training needs: Thorough training is needed for staff to master proficient and safe operation of various lifts and use of specialized lifting techniques. Refresher training is ongoing.
– Workflow adjustments: Incorporating lifts in patient care routines like bathing, transferring from ER to units etc. requires streamlining standardized practices.
– Staff resistance: Some caregivers prefer familiar manual methods and require education on risks, ergonomics, compliance and benefits of safer techniques.
Overcoming such issues requires commitment from management, funding support initiatives, dedicated trainers and consistent implementation over time with staff participation to instill safer practices as the norm. When addressed properly, facilities observe reduced injuries and high rates of lift utilization indicating a positive culture shift.
Mechanical patient lifts provide the optimal solution to address patient and caregiver safety concerns related to manual patient handling. With sizeable upfront investments but significant long term benefits in injury prevention, cost avoidance and regulatory compliance, transitioning to these assistive devices should be a priority for all healthcare facilities. Ongoing education, training, appropriate lift selection and standardized protocols help ensure they become fully integrated into daily patient mobility routines. This establishes an overall culture where safety is the top priority for staff as well as those receiving care.