With computer networking becoming increasingly ubiquitous, the Ethernet card has become an indispensable part of modern computing devices. An Ethernet card, also known as a network interface card (NIC), allows devices to connect to a local area network (LAN) and access resources like the internet, shared folders and printers wirelessly or through an Ethernet cable.
History and Evolution of Ethernet Cards
The history of Ethernet Cards dates back to the 1970s when Ethernet was first developed at Xerox PARC as an experimental local area network technology. In the early 1980s, 3Com shipped the first commercially available Ethernet cards for personal computers. These original Ethernet cards operated at a transmission speed of just 10 megabits per second (Mbps).
Throughout the 1980s and 1990s, Ethernet standards advanced through different generations with increased speeds – from 10BASE5 (thick Ethernet) to 10BASE-T (twisted pair Ethernet) to 100BASE-T (Fast Ethernet). By the late 1990s, most Ethernet cards supported speeds up to 100 Mbps. In 1998, the release of Gigabit Ethernet increased the standard connection speed to 1 gigabit per second (Gbps).
The past two decades have seen even faster Ethernet standards emerge with each generation. In 2003, 10 Gigabit Ethernet increased speeds to 10 Gbps. More recently, 40 Gigabit Ethernet and 100 Gigabit Ethernet cards have been developed capable of delivering 40Gbps and 100Gbps speeds respectively. Today, Ethernet has become the most widely installed local area network technology in use globally with speeds and throughput continuing to increase exponentially with each new standard.
Components and Features of Modern Ethernet Cards
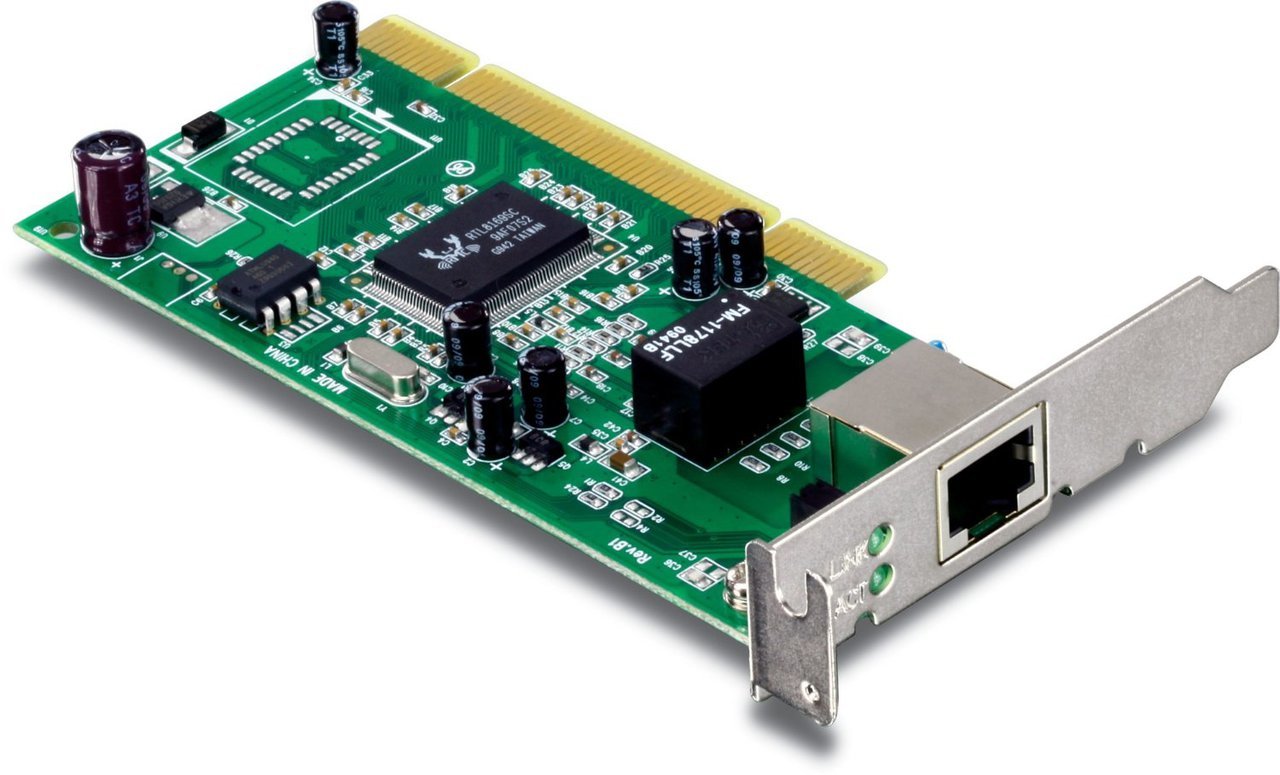
A modern Ethernet card consists of the following key components:
– Physical interface: This could be an RJ-45 Ethernet port for connecting to a twisted-pair cable or BiFi/BiDi optical ports for fiber connectivity. Wireless Ethernet cards use antennas for WiFi/Bluetooth connectivity.
– Ethernet controller chip: An application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) that handles the data link and physical layers of the Ethernet standard.
– Flash memory: Stores the MAC address and firmware for the Ethernet controller chip.
– SRAM/SDRAM: Provides buffer space for receiving and transmitting Ethernet frames. Faster memory enables higher throughput.
– Network processor: Handles tasks like traffic filtering, packet inspection, routing, Quality of Service etc. More advanced processors enable additional features.
– PHY transceiver: Physical layer transceiver that modulates and demodulates signals to interface with the physical Ethernet medium.
Key features offered by modern Ethernet controllers include multi-port/multi-queue support, hardware offloading for TCP/IP, RDMA, VxLAN, NVGRE, PCIe Gen 2-4 support, advanced traffic management, PTP hardware timestamping and more. High-performance Ethernet controllers are crucial for bandwidth-intensive applications.
Importance of Ethernet Cards in the Modern Computing Landscape
With the rise of big data, cloud computing, IoT and widespread network connectivity, Ethernet has become the de facto connectivity medium powering the digital world. Some key reasons why Ethernet cards remain central to modern computing systems:
– Ubiquitous connectivity standard: Ethernet is the most pervasive LAN technology globally, forming the backbone of enterprises, data centers, telecom networks and more.
– Ability to leverage existing infrastructure: Ethernet allows leveraging the vast installed base of IT infrastructure without requiring additional upgrades to support new devices.
– Scalability: Ethernet has scaled to support everything from small office networks to massive hyperscale data center networks with multi-terabit capacities.
– Backward compatibility: Newer Ethernet standards are designed to be compatible with older implementations, protecting existing investments.
– Performance and bandwidth: Continuous advances have ensured Ethernet remains the highest performance LAN technology, delivering multi-gigabit speeds required by modern applications.
– Features and capabilities: Modern Ethernet controllers integrate advanced offloads, QoS, telemetry and management features tailored for emerging workloads.
– Ubiquitous availability: Ethernet cards and controllers are commonly available across a wide range of computing devices from servers and PCs to switches and routers.
– Low cost of ownership: High-volume, mass-market availability has made Ethernet cards and components very cost-effective networking solutions.
As technology progresses into exabyte-scale data volumes and trillion sensor IoT deployments, the capabilities of Ethernet will continue to be stretched. The Ethernet card will therefore remain the fundamental physical and data link layer building block that enables all networked computing and communication systems globally.
*Note:
1. Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research
2. We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it