What are Aspheric Optics?
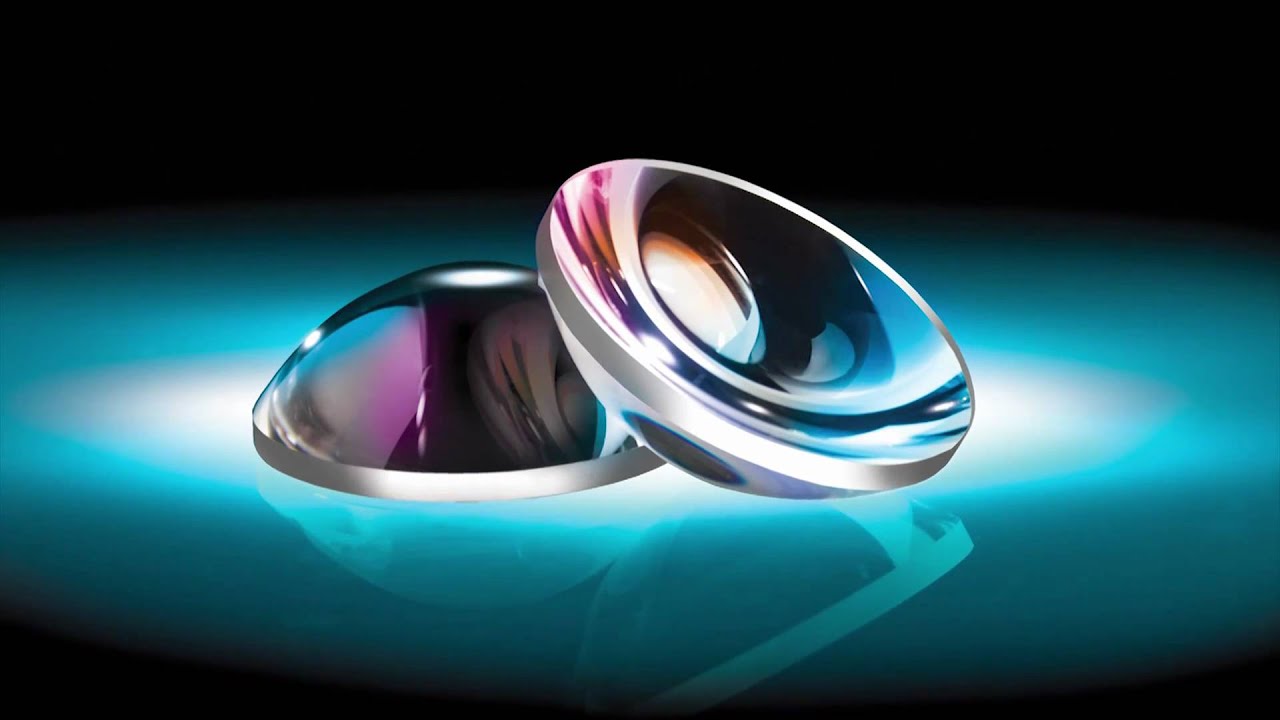
Aspheric Optics are advanced optical lenses that have a shape that is neither hemispherical nor ellipsoidal and deviates from the optical perfection of a spherical lens. Aspheric optics have a surface that is curved but doesn’t follow the contour of a perfect sphere.
Construction of Aspheric Optics
Most aspheric optics are made from glass, high-index plastic polymers or optical-grade fluoride crystals. Their surfaces are ground to very precise mathematical aspheric formulas using computer numerical control machining tools. This gives the lens its unique non-spherical shape that helps correct aberration. Special lens polishing techniques are also used to finish the Aspheric Lenses surfaces and ensure their optical accuracy.
Aberration Correction Using Aspherics
Conventional spherical lenses suffer from optical aberrations like spherical aberration, coma and astigmatism. Aspheric optics are designed in non-spherical shapes to counteract these aberrations. Their precise aspheric form bends light in a way that offsets spherical aberration. This allows aspheric optics to deliver sharper, clearer images over both their center and peripheral areas compared to spherical lenses.
Uses of Aspheric Lenses in Photography
Aspherics are commonly used in compact camera lenses, SLR camera lenses and cine lenses. Their ability to reduce spherical aberration without increasing optical complexity allows camera lenses to be smaller in size while maintaining good image quality. Aspheric elements in zoom lenses also help correct optical aberrations throughout the variable focal lengths. This enhances zoom sharpness and contrast. Many pro-grade camera lenses contain sophisticated aspheric designs for optimum performance.
Applications in Microscopy
Due to their high precision optical surface profiles, aspherics play a key role in high-power microscope objectives and eyepiece lenses. Their distortion-free imaging capabilities allow microscopes to achieve magnifications up to 1000x with superb resolution and contrast. Aspheric doublets and triplets compensate for spherical aberration at all points on microscope slides, delivering consistently clear viewing. Advanced cell biology microscopy relies on sophisticated aspheric optics designs.
Benefits in Spotting Scopes and Binoculars
Aspherics enable compact spotting scope and binocular designs while maintaining wide fields of view and edge-to-edge sharpness. Their use in roof prism binoculars helps counteract chromatic aberration for brilliant color rendition. Aspheric lens combinations in spotting scopes deliver high resolution and contrast across the entire viewing angle from center to periphery. Both amateur and professional spotting optics contain optimized aspheric lens configurations.
Role in Projector and Telescope Optics
Multi-element aspheric lens systems are found in video and data projector optics where they correct various optical distortions across large imaging areas. Aspheric lens barrels in reflecting telescopes minimize off-axis aberrations, capturing more light and enlarging observed views with optimum clarity and brightness. Advanced ground-based and space telescopes feature complex aspheric lens designs optimized through rigorous modeling.
Application in Smartphone and Tablet Cameras
Today’s compact digital cameras, internet-connected smartphones and tablets feature advanced aspheric lens elements that allow small form factors while providing large apertures and wide-angle views. Aspheric lens pairs or triplets correct geometric distortion as well as chromatic aberrations across the entire image sensor area. They are a critical part of achieving high resolution and natural perspective in miniature camera modules.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Aspheric lenses allow optical systems to be more compact while achieving higher performance levels. However, manufacturing aspheric surfaces demands precision computer numerical control grinding and polishing methods, which increases lens production costs. Aspherics may also exhibit coma at large apertures if not optimized well through optical design modeling. But their ability to reduce aberrations without resorting to complex lens assemblies makes them invaluable in today’s advanced optical instruments.
Aspheric lenses employ precisely shaped non-spherical surfaces to counteract optical aberrations like spherical aberration, coma and astigmatism. This aberration correction capability has enabled more compact yet high-performance optical designs across diverse applications in photography, microscopy, astronomy and consumer electronics. Advances in precision machining have made sophisticated aspheric surfaces feasible for commercial production. Though costly to manufacture, aspheric optics remain an important optical technology driving continued miniaturization with no compromise in image quality.
*Note:
1. Source: Coherent Market Insights, Public sources, Desk research
2. We have leveraged AI tools to mine information and compile it.